

Multiple infections in women can lead to reproductive complications. Repeat infections are common, particularly in women. It is important to complete your antibiotic treatment, since inappropriately treated partners can pass on the disease. If your symptoms do not subside after a few days of taking antibiotics, visit your healthcare provider. Refrain from sexual activity until your antibiotic course is completed. If your test is positive, talk to your healthcare provider. Gonorrhea is easily treated with dual antibiotics. Ensure that any recent sexual partners are aware of your diagnosis so they can also request testing.Ĭhlamydia is easily treated with antibiotics. Abstain from sexual contact until the completion of the antibiotic course.
GONORRHEA SYMPTOMS IN MALES PROFESSIONAL
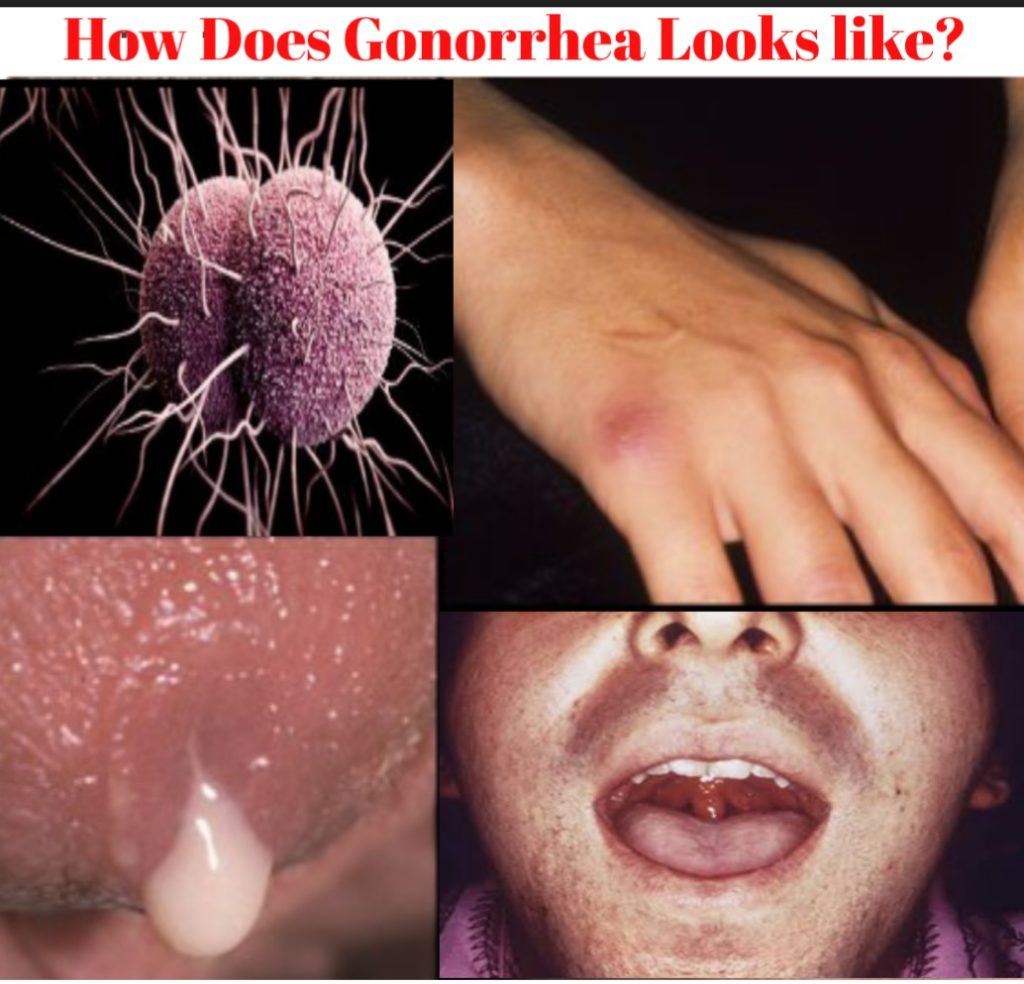
If I get a positive result, what should I do next?Ĭontact a health professional to begin a course of prescribed antibiotics as soon as possible. Although antibiotic treatment is effective for the current bacterial infection, it does not prevent future infections through exposure to an infected individual. Treatment is simple and effective and will prevent any complications associated with these STDs. NAAT tests are the most sensitive and can be performed rapidly.Ĭhlamydia and gonorrhea are common STDs, particularly in individuals aged between 15 and 24 years, but many infected individuals remain asymptomatic. Our lab uses a molecular testing technique known as nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT), which detects the presence of bacterial DNA from a urine sample or a vaginal swab. Several different diagnostic tests are available for chlamydia and gonorrhea. To take a urine sample, use the collection cup provided and transfer a small amount of the urine into the sample vial.Place your sample in the specimen bag provided and mail it back to the lab using the prepaid envelope inside the kit. How does the Chlamydia and Gonorrhea Test work? Chlamydial and gonorrheal infections also facilitate the transmission of HIV infection. Other potential complications include gonococcal bacteremia, pharyngitis, and reactive arthritis. Untreated chlamydia during pregnancy has been associated with preterm delivery, and untreated gonorrhea during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage and inflammation of the lining of the uterus.Ĭomplications in untreated males can include epididymitis, sterility, and prostatis. In females, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and PID-associated infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain can occur. These STDs can also be transmitted from a mother with an untreated infection to her newborn during childbirth, increasing the risk of chlamydial conjunctivitis and pneumonia, and gonorrhea-associated eye infections and sepsis.Īlthough many infected individuals do not show any symptoms, untreated chlamydial and gonorrheal infections can lead to serious health complications. They are transmitted through sexual contact with the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus of an infected individual.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
